As someone who knows a lot about proxy servers, I want to help you understand that there are many different types of proxies out there.
Each kind works differently because of where it is, how it handles your internet traffic, how private it keeps you, and what kind of IP address it uses. It’s really important to think about what you need from a proxy before picking one.
This will help you make sure you’re getting the best protection online. Let’s explore more about the different proxies and figure out which one is right for you. Keep reading to learn more!
Types of Proxies Based on Traffic Flow
Proxy servers can be classified as forward or reverse proxies based on whether they are set up as outgoing or incoming on the client’s side.
1. Forward Proxy – Hides Your Identity
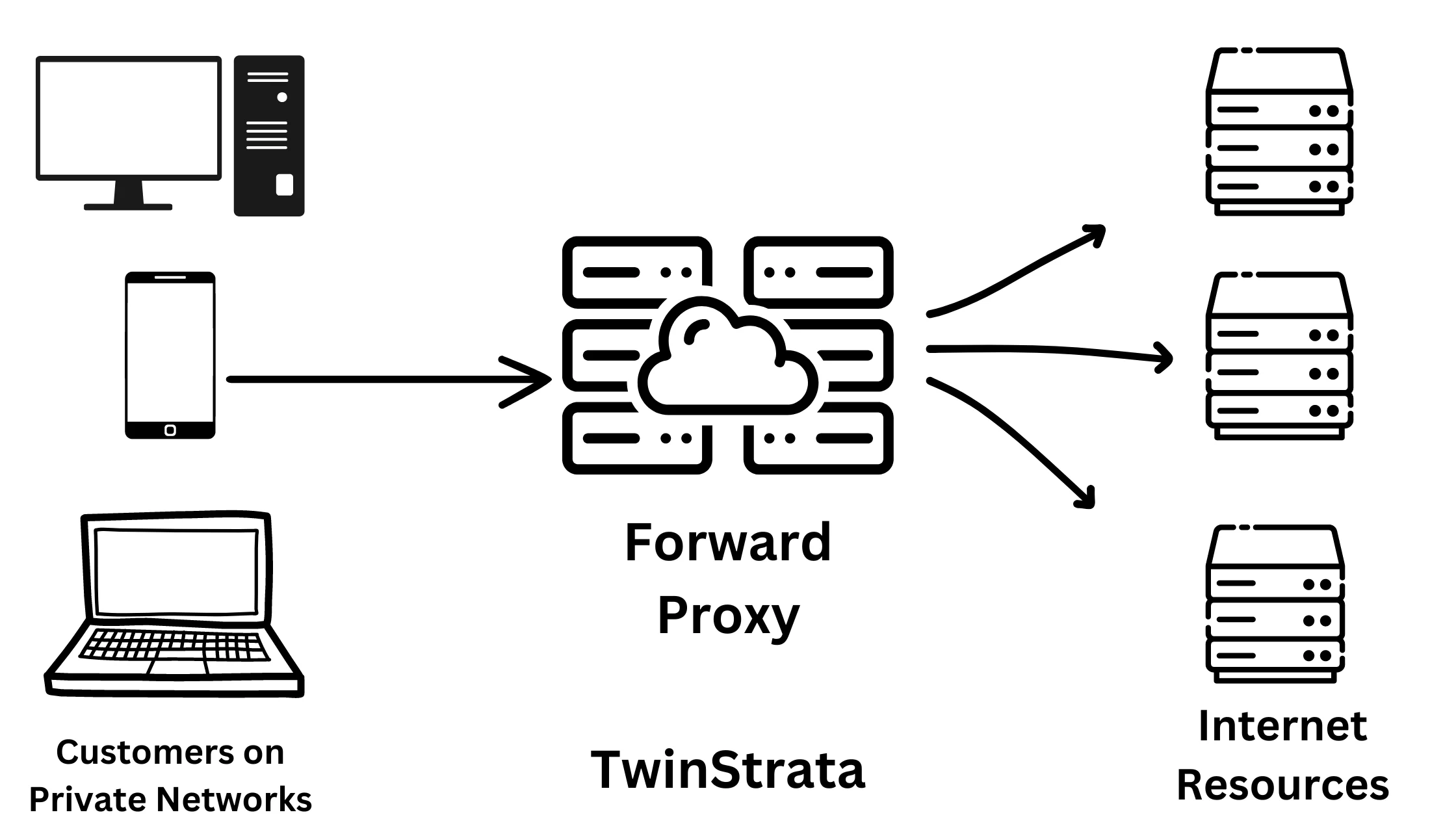
Proxy servers act as representatives of their original clients, taking inbound traffic and forwarding it to their final destination. The IP addresses of the initial requests are masked in order to retrieve resources anonymously from public networks.
2. Reverse Proxy – Speeds Up Load Times
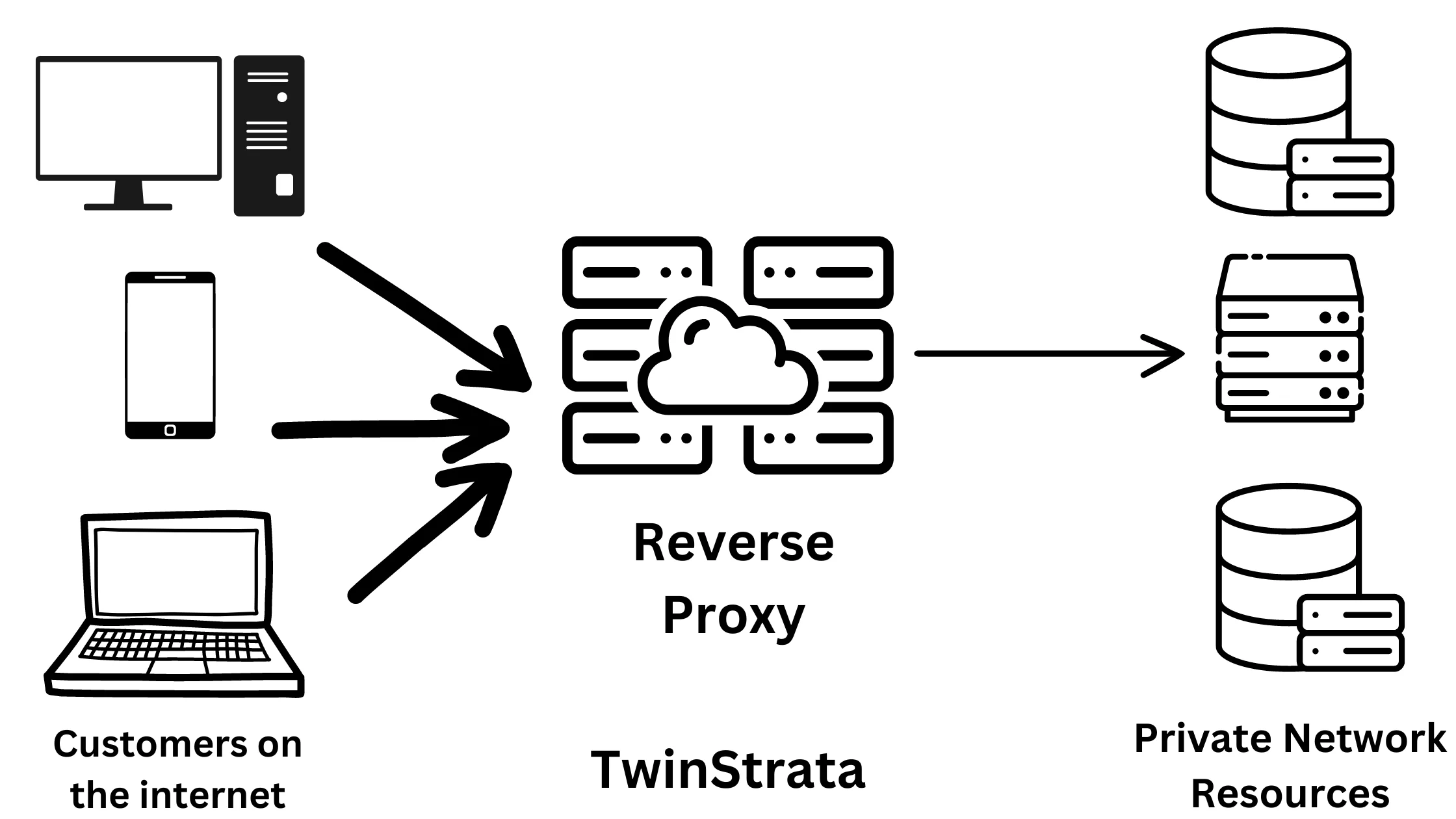
Reverse proxies serve several important functions to protect and optimize the operation of web servers.
They evenly distribute incoming requests among multiple servers, ensuring that no single server gets overwhelmed by traffic.
Additionally, they act as a front-line defense against Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, which are attempts to flood a server with excessive requests to disrupt its normal operation.
Beyond load balancing and security, reverse proxies can also perform other useful tasks. They can store copies of web pages (caching) to make them load faster for users who request the same content repeatedly.
They can handle user authentication, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access certain resources. Reverse proxies can also decrypt encrypted data, compress files to save bandwidth, and optimize content for faster delivery to users.
These functions collectively improve the performance, security, and efficiency of web servers and the websites they host.
Proxies are based on anonymity level.
The server’s anonymity level is another important consideration when choosing a proxy, as it hides the headers that you send. Your request headers may be forwarded in full or in part, or the headers may be removed or changed.
1. Transparent Proxy – Level 3 – Faster website retrieval:
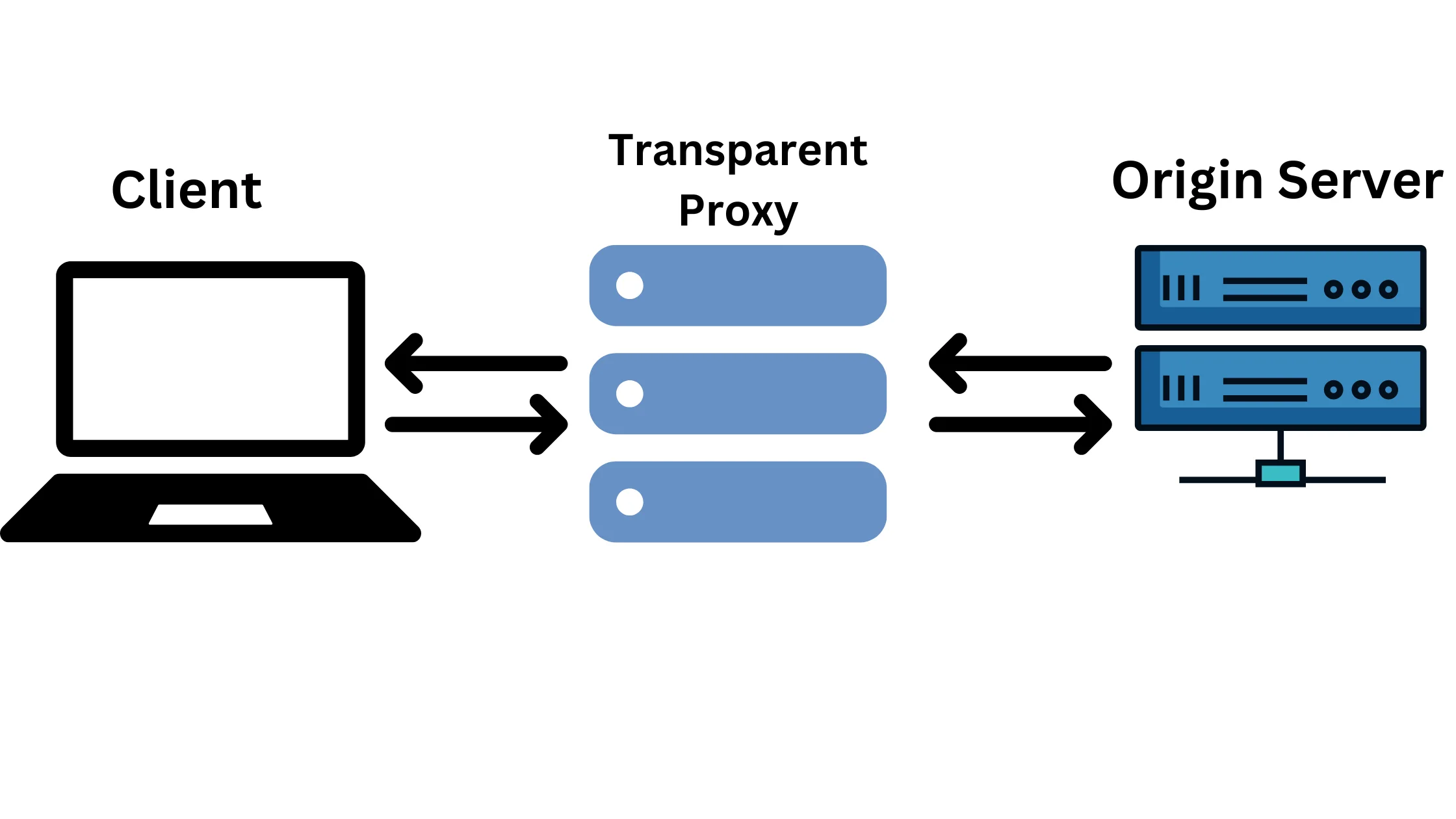
These proxies are mainly used to speed up website loading and don’t focus on keeping your identity hidden. They store copies of frequently visited websites to make them load faster.
However, when you use them, your real IP address is still visible to websites.
2. Anonymous Proxy Level 2 – Faster Internet Browsing:
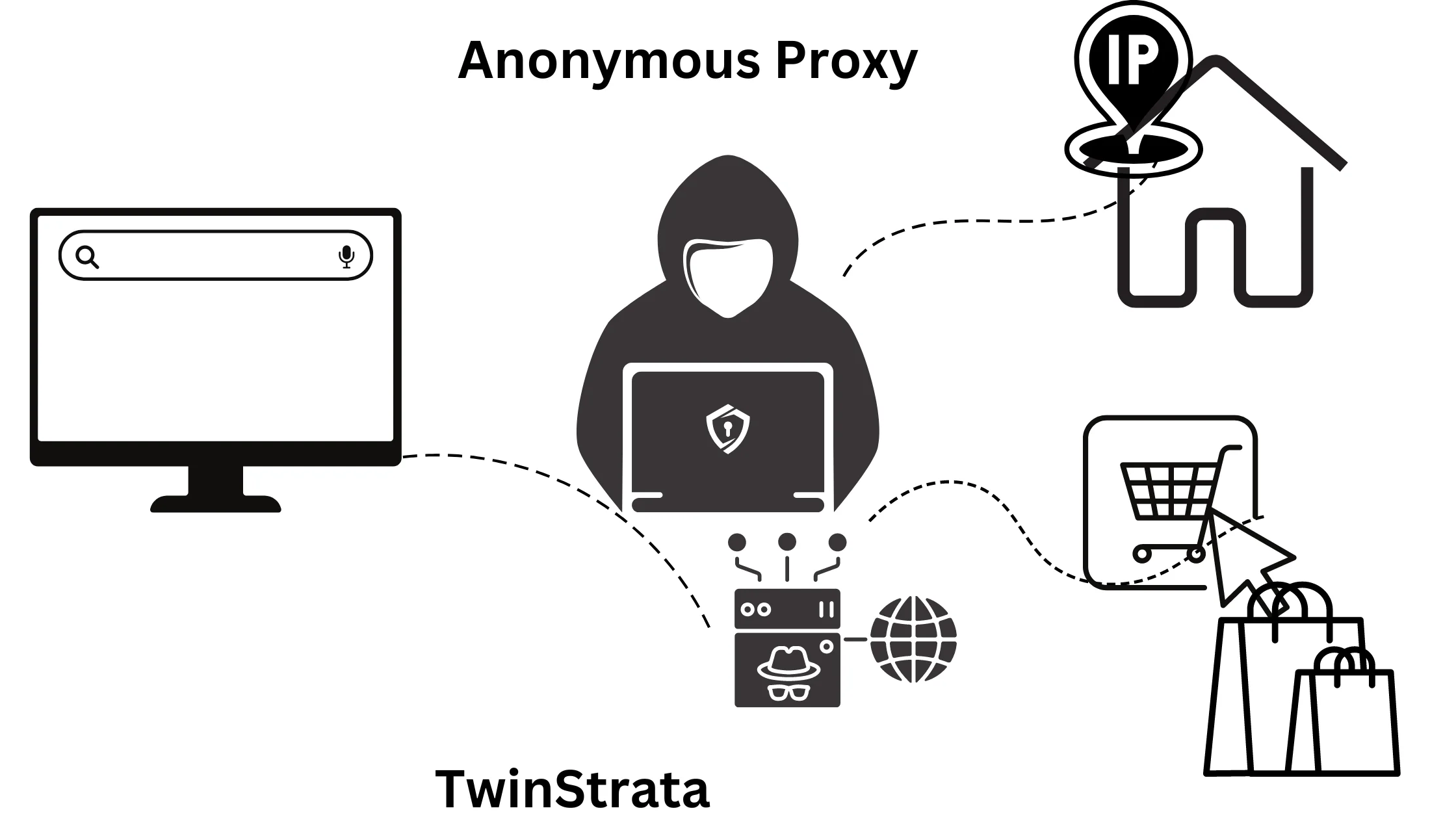
These proxies, also called distorting proxies, hide your actual IP address and location from websites you visit.
However, they do let websites know that you’re using a proxy. They are popular because they provide a good balance between anonymity and speed for everyday internet use.
3. Anonymity Level: Level 1 Elite Proxy:
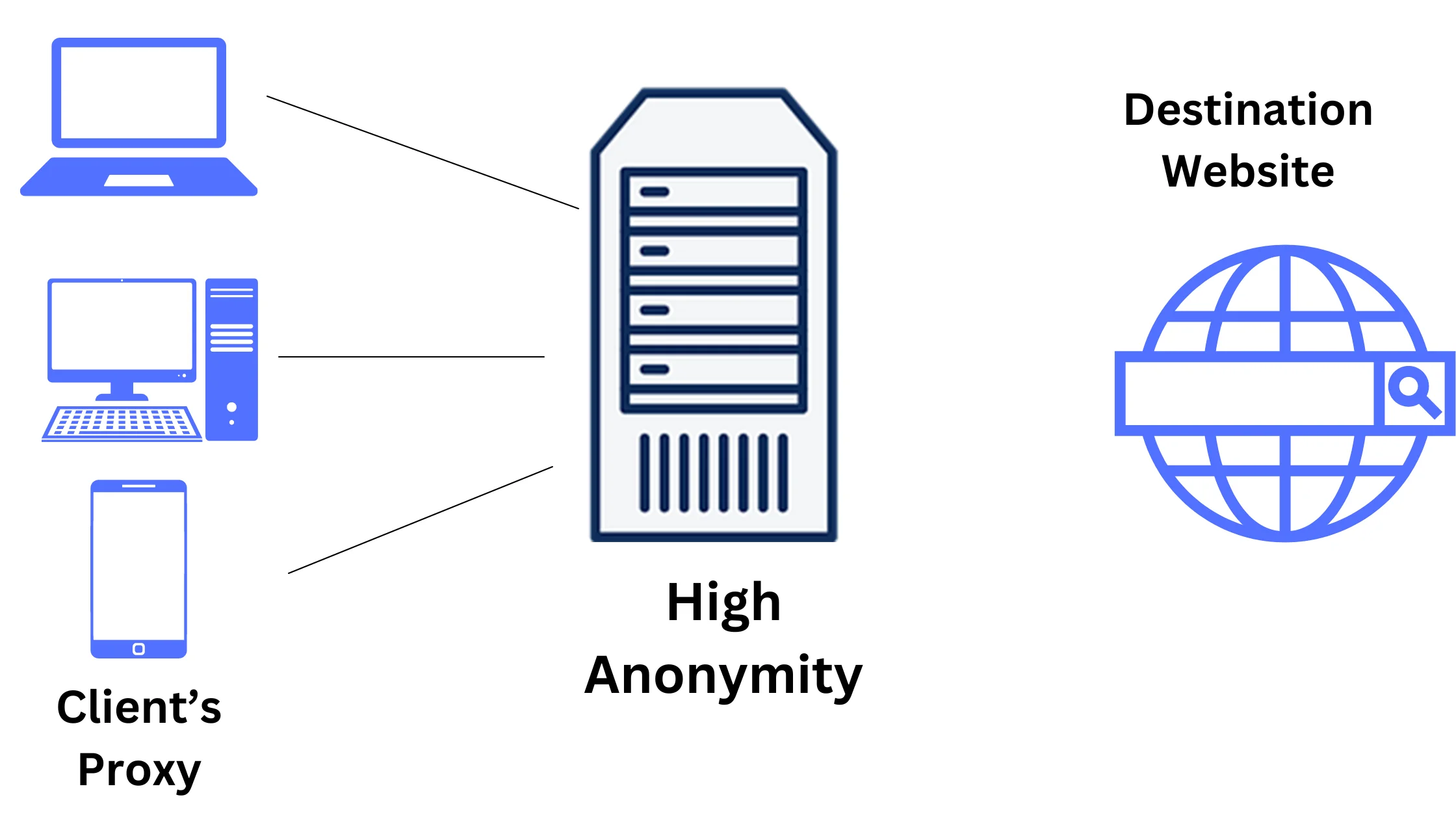
For maximum anonymity and security, you should opt for a Level 1 elite proxy. It not only hides your IP address but also conceals the fact that you’re using a proxy.
When you use this type of proxy, websites see your requests as if they’re coming from regular users, as it removes certain information (the ‘Via’ field) in the HTTP header that indicates proxy usage.
This makes it the best choice for keeping your online activities private.
Proxies are based on IP location.
There are several types of proxies, according to the IP address your proxy server provides.
1. Data Center Proxy – For Quick and Short Tasks:
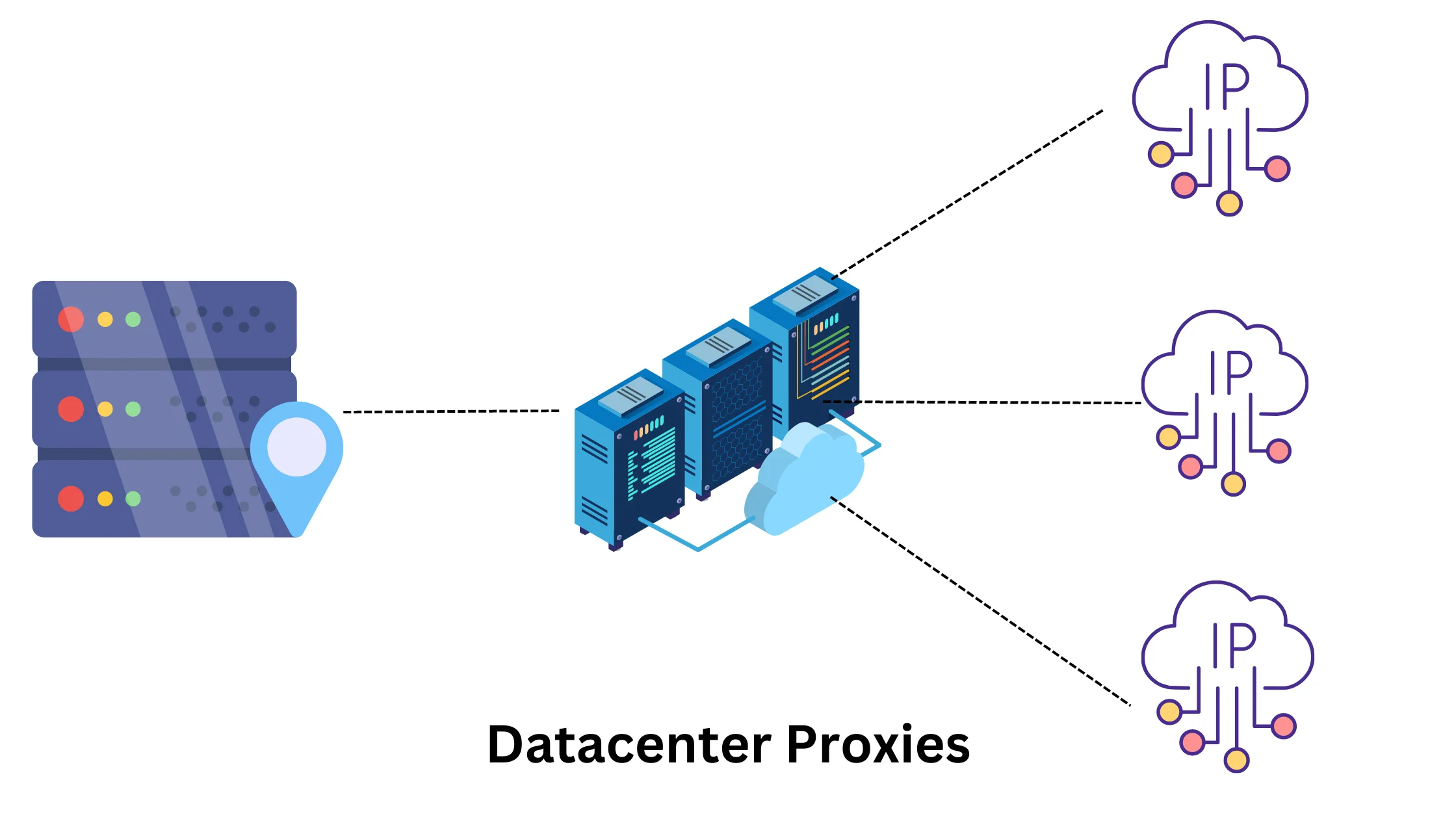
Data center proxies get their IP addresses from large server farms, which makes them fast but also increases the risk of being blocked for data-heavy activities. They are cost-effective.
Example: If you need to quickly check prices on a shopping website or access some basic information online, a data center proxy can help you do that speedily.
2. Residential Proxy – For Geo-Location Masking:
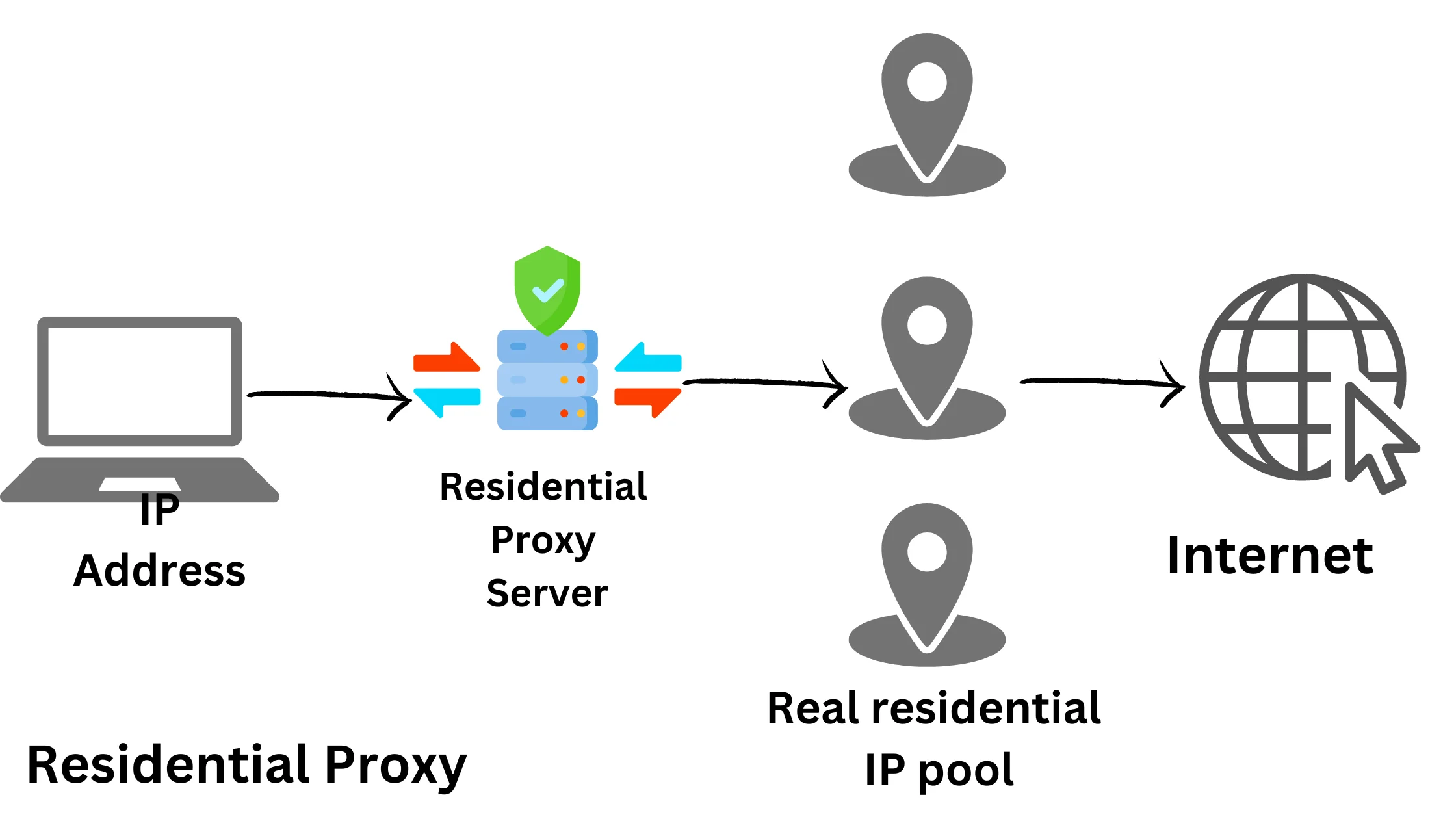
Residential proxies provide IP addresses from internet service providers (ISPs), making it seem like you’re a regular internet user. This means websites won’t easily detect that you’re using a proxy, making them great for accessing restricted content.
Example: If you want to watch region-locked videos on a streaming platform, a residential proxy can help you appear as if you’re in the right location.
3. Mobile Proxy – For Mobile Ads and App Testing:
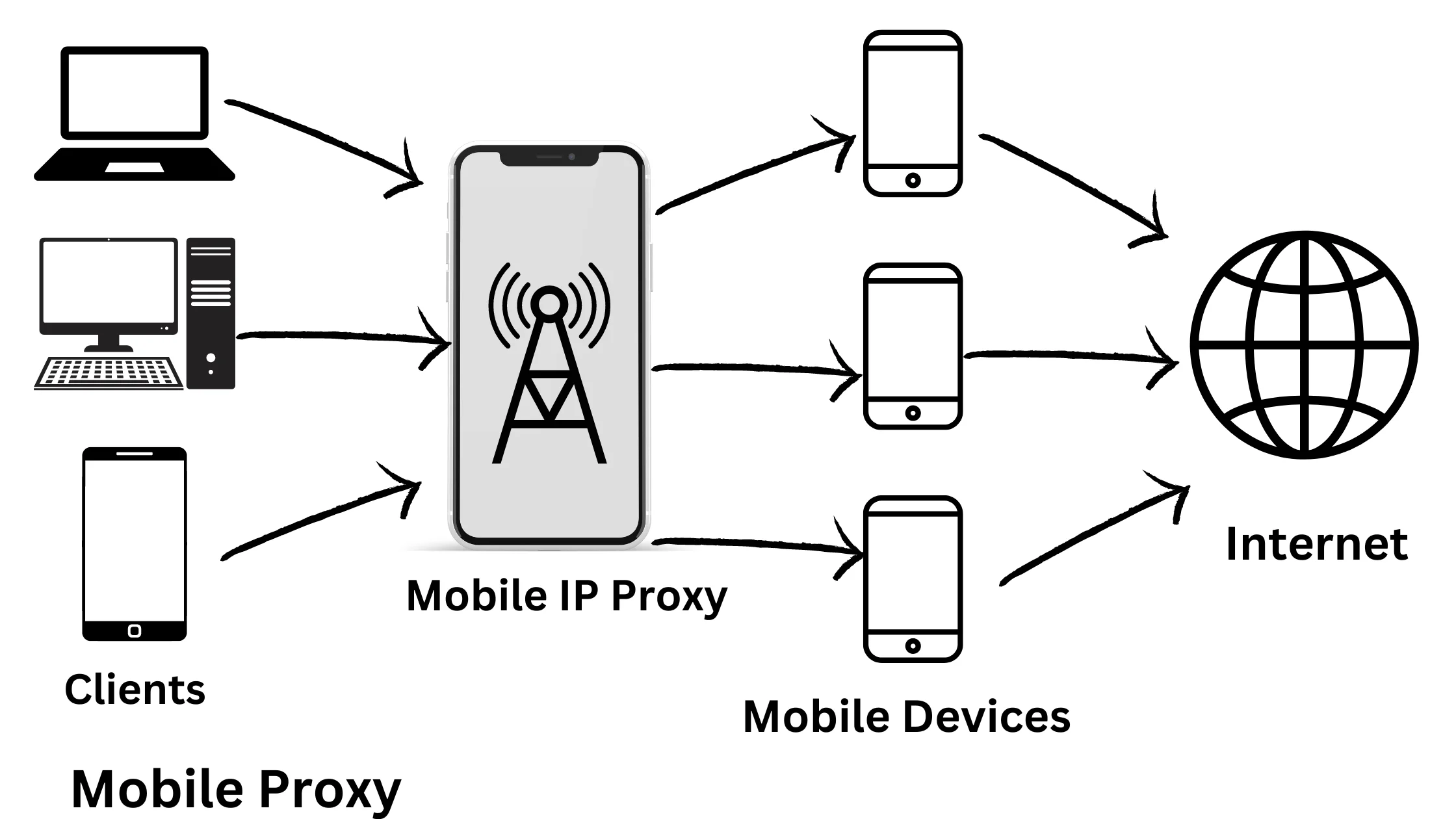
Mobile proxies, like 3G and 4G proxies, use IP addresses from mobile users. They make it look like you’re accessing the internet from a mobile device, even if you’re on a desktop computer. These proxies are handy for testing mobile apps and advertisements.
Example: If you’re a developer testing a mobile app or running mobile-specific ads, a mobile proxy can simulate the experience of a real mobile user.
Types of Proxies Based on Protocol
Proxies can play a role in enhancing and securing various network protocols at the application level:
1. HTTPS (SSL) Proxy – Cyber Security:
Many websites and services use SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) to encrypt data between clients and servers, ensuring security. SSL proxies are highly secure because they encrypt and decrypt all data passing through them, providing strong protection against cyber threats.
Example: When you log in to your online banking account, an HTTPS proxy helps ensure that your sensitive information is encrypted and safe from prying eyes.
2. HTTP Proxy – Sneaker Copping:
HTTP is a common internet protocol, but it lacks security features and sends data in plain text. While it’s becoming less popular for general use due to security concerns, it’s still useful for specific tasks like “sneaker copping,” which involves buying limited-edition shoes.
Example: Sneaker enthusiasts might use HTTP proxies to access websites where they can purchase rare sneakers because they don’t require high security.
3. SOCKS5 Proxy – Streaming, Gaming, Torrenting:
SOCKS5 proxies work at a lower level compared to HTTP(S) proxies. They transmit data without inspecting it.
This makes them versatile for handling various types of internet traffic, including gaming, streaming, and torrenting. They’re also faster at sending unencrypted data, especially when using the UDP protocol.
Example: Gamers might use SOCKS5 proxies to reduce lag and improve their gaming experience by routing their traffic through servers optimized for gaming.
Types of Proxies Based on Specific Applications
Proxies are used for specific purposes in different situations, such as taking on the roles of DNS servers or handling email transfers:
1. DNS Proxy – Better Speed and Performance:
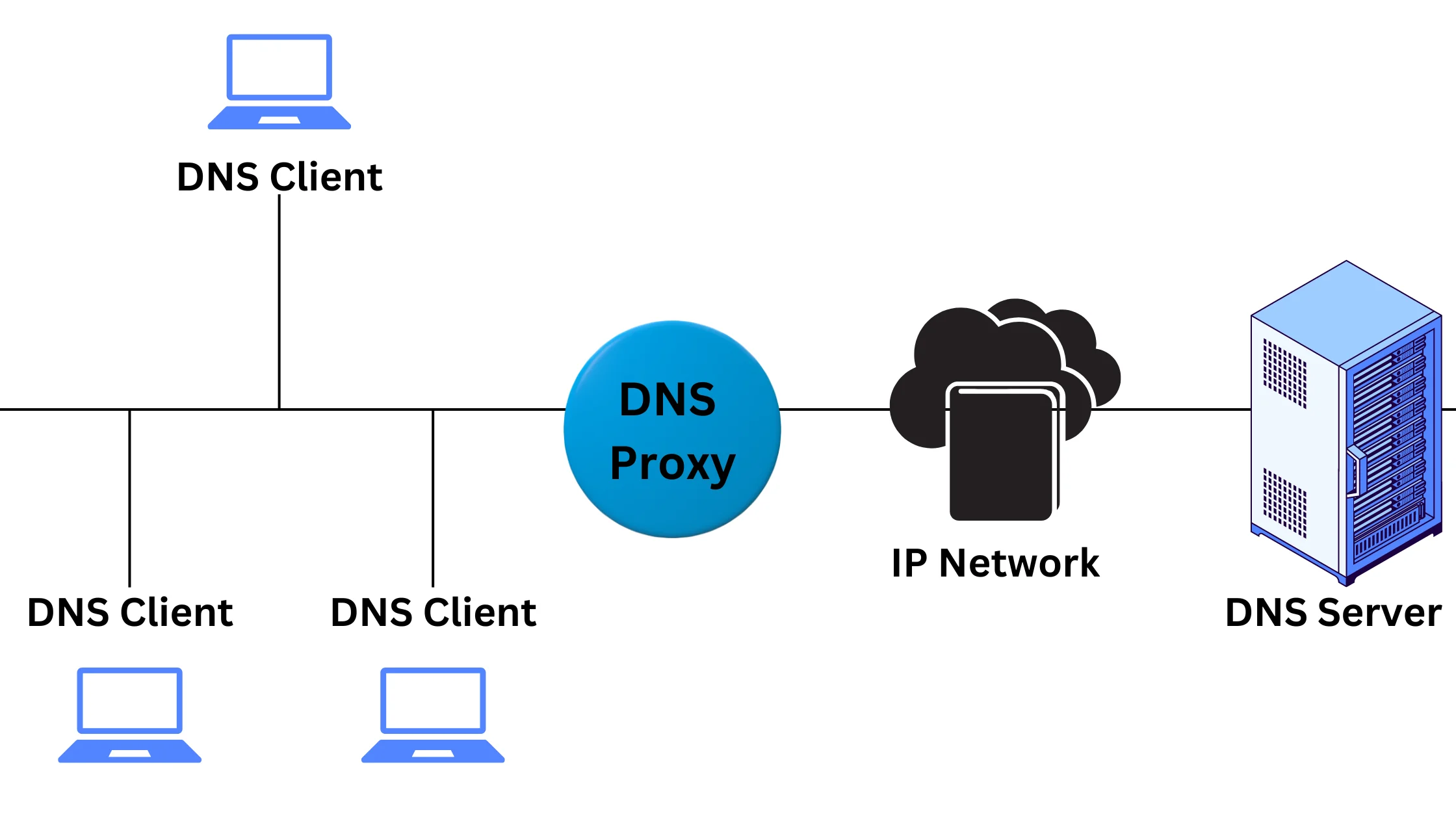
DNS proxies can act like DNS servers, making the process of finding websites faster and more efficient. They can store and forward queries quickly. Some smart DNS proxies also help you access blocked websites, similar to VPNs.
Example: When you type a website address in your browser, a DNS proxy can help find the website’s location more quickly, improving your internet experience.
2. SMTP Proxy – Anti-Spam Features:
SMTP proxies serve as intermediaries for email transfers, especially useful when dealing with spam or malware. They filter incoming and outgoing email traffic, controlling the rate to reduce unwanted emails.
Example: An SMTP proxy can help prevent your email inbox from getting flooded with spam messages by filtering out malicious emails.
3. TOR Onion Proxy – Secure Internet Surfing:
The TOR network provides anonymity by routing your Internet traffic through volunteer servers. To hide both your entry and exit points on the TOR network completely, you can use an additional proxy server along with TOR.
Example: If you want to browse the internet anonymously and ensure that your connection points are fully hidden, you might use a TOR onion proxy in addition to the TOR network.
4. Proxies for SEO – Anonymous SEO campaigns:
Proxy servers are essential for large-scale SEO tasks requiring anonymity, speed, and security reliability. They help hide your identity when conducting SEO-related web scraping and analysis, preventing target websites from blocking your IP address.
Example: If you’re an SEO professional, you can use SEO proxies with various tools to gather data and analyze your competitors’ websites without revealing your identity.
Types of Proxies Based on Service
There are three main types of proxies based on how many people use the same IP address(es) provided by the proxy service:
1. Public Proxy – Free for Everyone:
Public proxies are available to anyone for free. They are often found on websites that list proxy servers.
However, they have many drawbacks: they tend to be unreliable, slow, and not very secure. The only advantage is that they are free to use.
Example: Some websites offer lists of public proxies that you can use to access blocked content, but they may not always work well.
2. Private Proxy – Exclusive to One User:
Private proxies are dedicated to a single user, providing reliability (no interruptions), high speeds (minimal impact on your connection), and better security (you know who is handling your data).
They typically require a monthly subscription fee, but you get additional features and better performance.
Example: Companies may use private proxies to secure their data and ensure a stable internet connection for their employees.
3. Shared Proxy – Used by a Group of Users:
Shared proxies are a middle-ground option. They are cheaper than private proxies and are provided by private companies to a group of users.
They offer good security and reliability but may have slightly slower speeds because multiple users share the same IP address.
Example: When multiple people in a household want to access region-restricted content, they can use a shared proxy to do so, but the internet speed may be slightly affected.
Types of Proxies Based on Rotation
Proxies can be divided into two types based on whether they change their IP address or not:
1. Static Proxy – Simulates a Single Unique User:
A static proxy uses just one residential IP address to hide your own. This makes you look like a regular and real user, keeping your identity hidden. However, you can only access content from the location of the proxy’s IP address.
Example: If you use a static proxy with an IP address in New York, websites will think you’re in New York, even if you’re somewhere else.
2. Rotating Proxy – Uses a Pool of Different IPs:
Rotating proxies is useful when you need a variety of IP addresses from different locations, like for web scraping. With a rotating proxy, you get assigned a new IP address each time you make a new connection or after a certain period.
Example: If you use a rotating proxy, you might have one IP address from New York, then another from London, and so on. This helps you access a wide range of content from various locations.
Different proxies at a glance:
| Type of Proxy | Main Use | Example of Use | Example Provider |
| Forward Proxy | Hides user’s identity | Accessing internet anonymously | Squid Proxy |
| Reverse Proxy | Speeds up load times improves security | Balancing load on servers | Nginx |
| Transparent Proxy | Speeds up website retrieval | Caching frequently visited websites | Apache Traffic Server |
| Anonymous Proxy | Hides your IP, reveals proxy use | General web browsing with privacy | HideMyAss |
| Elite Proxy | Provides high anonymity | Sensitive online activities | Luminati |
| Data Center Proxy | Quick tasks, risk of being blocked | Quick price checks | MyPrivateProxy |
| Residential Proxy | Geo-location masking | Watching region-locked streaming content | Smartproxy |
| Mobile Proxy | Mobile ads and app testing | Testing mobile apps | Oxylabs |
| HTTPS (SSL) Proxy | Enhancing cyber security | Secure online banking | SSLPrivateProxy |
| HTTP Proxy | Specific tasks like sneaker copping | Buying limited-edition shoes | Blazing SEO |
| SOCKS5 Proxy | Streaming, gaming, torrenting | Reducing lag in online gaming | IPVanish |
| DNS Proxy | Speeding up the internet, accessing blocked websites | Faster website access | Smart DNS Proxy |
| SMTP Proxy | Filtering email spam | Reducing email spam | Proximify |
| TOR Onion Proxy | Secure internet surfing | Anonymous Browsing | Tor Project (with proxy) |
| SEO Proxy | Anonymous SEO campaigns | Web scraping for SEO analysis | Storm Proxies |
| Public Proxy | Free access to blocked content | Casual browsing with access to blocked content | Public proxy lists online |
| Private Proxy | Exclusive, secure, and reliable internet access | Business data security | Proxy-Seller |
| Shared Proxy | Cost-effective for a group of users | Household access to region-restricted content | Highproxies |
| Static Proxy | Simulates a single-user | Consistent online presence | NetNut |
| Rotating Proxy | Accessing a wide range of IPs for scraping | Web scraping across different regions | RotatingProxies |
Quick Links:
- Datacenter Proxies vs Residential Proxies
- Proxy vs VPN Comparison
- Reverse Proxy vs Forward Proxy
- How to Test Proxies?
Conclusion: Types of Proxies and Their Uses on 2025
There are indeed many types of proxy servers, and choosing the right one can be overwhelming because each user has different needs.
To make it easier, I’ve categorized the proxy types based on how they are used and what they’re good for. So, read carefully to find the best proxy that suits your specific requirements.
